How to Build an AI Agent with ChatGPT: A Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide for 2025

How to Build an AI Agent with ChatGPT: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
-
- Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how we interact with technology by enabling AI agents that think and act autonomously.
-
- Building an AI agent with ChatGPT involves defining clear goals, selecting the right technology, and customizing the AI to your needs.
-
- Choose between a flexible, code-based stack or user-friendly no-code platforms depending on your skills and project requirements.
-
- Leverage OpenAI’s advanced GPT-4 model, fine-tune with your own data, and use retrieval techniques like RAG for up-to-date responses.
-
- Build user interfaces that provide smooth interactions and ensure thorough testing before deploying across multiple channels.
- Monitor, iterate, and expand your agent’s capabilities, embracing autonomous tool use and advanced workflows as you grow.
Table of contents
What is an AI Agent and Why Build One with ChatGPT?
Before diving in, let’s clarify what an AI agent is. Simply put, an AI agent is a program designed to perform specific tasks autonomously — this could be anything from answering customer questions to managing workflow automation. When powered by ChatGPT, these AI agents gain the remarkable ability to understand natural language, reason through problems, and respond in a humanlike way.
With OpenAI’s latest models like GPT-4, developers can now create agents that do more than just react; they can think, plan, and execute tasks proactively by connecting to external tools or data sources. This opens up endless possibilities for automating repetitive work, enhancing user experience, and improving business efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your AI Agent’s Purpose
The foundation of a successful AI agent is a clear purpose. According to the step-by-step guide from ClickUp Blog, your first job is to define the agent’s goals and how it will interact with users.
Start by answering these questions:
-
- What tasks will the AI handle? This could be answering FAQs, managing customer support tickets, summarizing reports, or even generating content.
-
- Who are the users? Are they customers, sales teams, internal support staff, or website visitors?
-
- What data will it use? Examples include CRM records, support queries, product documents, or knowledge bases.
- How will it communicate? Will it chat in real-time, send emails, or use voice commands?
Mapping out the decision tree of possible user interactions ensures that your agent knows how to respond appropriately in every situation. This helps avoid confusion and keeps conversations smooth.
Step 2: Choose Your Technology Stack or No-Code Platform
Next, you’ll decide how to build your AI agent — using traditional coding or a no-code platform. The choice depends largely on your technical skills, timeline, and customization needs.
Code-Based Tech Stack
For developers, the backend often includes:
-
- Python programming language.
-
- The OpenAI API to access GPT-4 and other models.
-
- Frameworks like LangChain or FastAPI for building conversational workflows and web apps.
-
- Databases such as PostgreSQL or MongoDB to store session data.
-
- Cloud hosting providers like AWS or Azure.
- Integration tools like Zapier for automation.
This stack offers maximum flexibility to tailor the AI agent precisely to your needs (source: ClickUp Blog).
No-Code Platforms
If coding isn’t your thing or you want faster results, several user-friendly platforms allow you to create AI agents via drag-and-drop interfaces:
| Platform | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| OpenAI Agent Builder | Uses ChatGPT to auto-generate prompts, design workflows, test, deploy. | Beginners, quick prototypes (YouTube 1, YouTube 2) |
| Botpress | Knowledge base integration, multi-channel support (WhatsApp, Slack), lead workflows. | Production bots for customer-facing use (YouTube 1) |
| Zapier AI Agents | Multiple app integrations, scalable automation without heavy markup. | Internal tools, rapid scaling (YouTube 1) |
OpenAI’s official guide encourages teams to start simply, then grow functionality over time (source: OpenAI PDF Guide).
Step 3: Set Up and Configure the AI Model
After choosing your platform, it’s time to access the OpenAI API and configure your model. GPT-4 is highly recommended for building AI agents because of its advanced reasoning and memory capabilities (source: ClickUp Blog and OpenAI Announcement).
Here’s a simple Python example showing how you might make a basic API call to GPT-4:
import openai
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What’s the weather today?"}]
)
print(response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"])
This snippet sends a user question to ChatGPT and prints the reply. You can expand this by adding context, session state, or even letting the AI select tools to act autonomously, a feature introduced with ChatGPT agents that empowers “thinking and acting” capabilities (source: OpenAI Introducing ChatGPT Agent).
Furthermore, ChatGPT itself can auto-generate prompts tailored for your agent, speeding up development (source: YouTube Tutorial).
Step 4: Customize and Train Your AI Agent
While ChatGPT is powerful out-of-the-box, you’ll want to fine-tune your agent for domain-specific knowledge and brand voice.
Upload Custom Data
Using OpenAI’s fine-tuning API, you can upload your own datasets such as frequently asked questions, standard operating procedures, and product manuals. Training your agent on this data makes responses more accurate and relevant to your users’ needs (source: ClickUp Blog).
Connect Knowledge Bases
Another popular technique is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), that connects your AI directly to documents, PDFs, websites, or tools like Notion. This lets the agent fetch real-time, up-to-date information rather than relying solely on pre-trained knowledge (source: YouTube Tutorial).
Set Rules and Boundaries
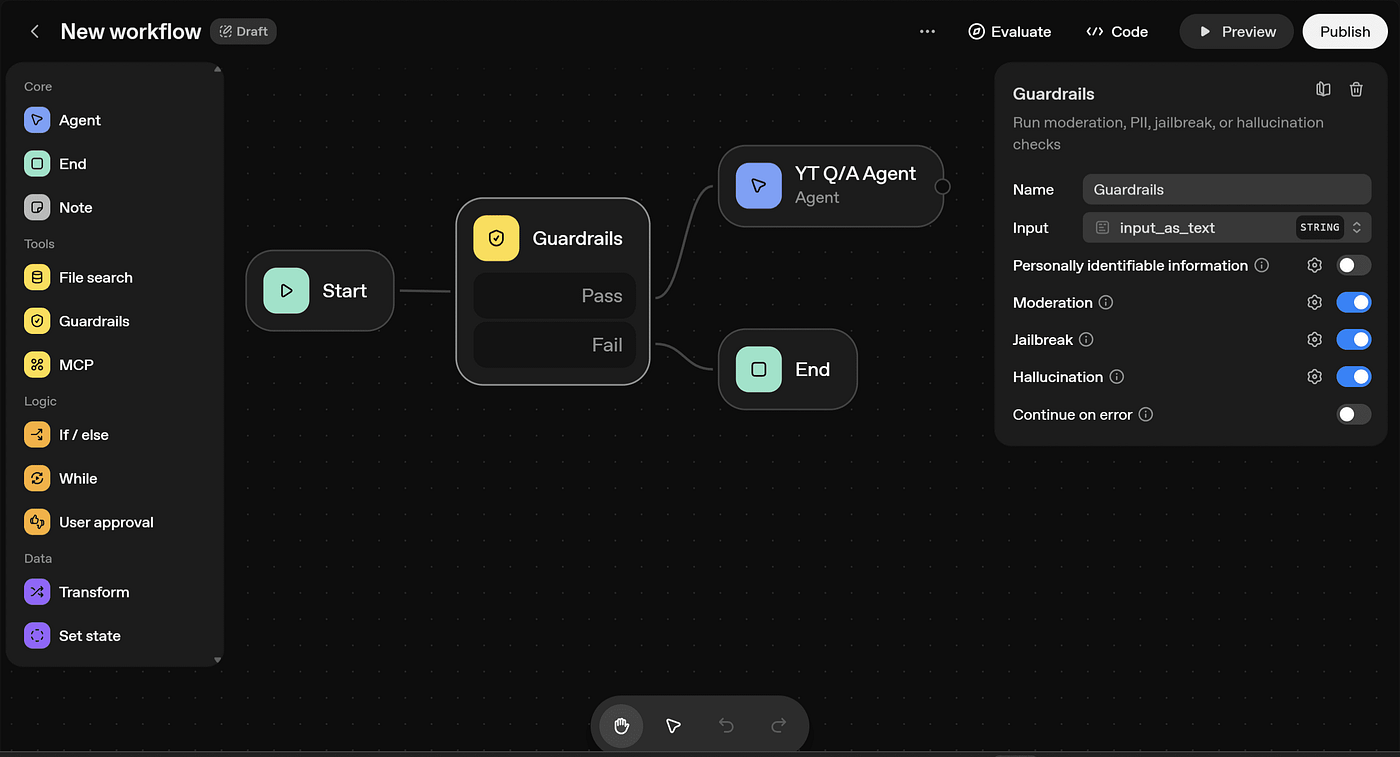
Establish your agent’s tone, logic, and behavior with programming constructs such as schemas, guardrails, and loops to ensure consistent and safe interactions (source: YouTube Tutorial).
Additional advanced features you can implement include:
-
- File searching capabilities.
-
- URL handling for external data fetching.
-
- Data transformation and approval checkpoints.
- State variables to remember ongoing conversations.
All these tools help your AI agent behave intelligently and reliably.
Step 5: Build the User Interface and Interaction Logic
Once the AI backend is ready, you need a smooth interface for users to access your agent.
-
- UI Development: Many developers use web frameworks like FastAPI to create user-friendly dashboards or chat widgets that integrate with the AI backend (source: ClickUp Blog).
-
- Workflows and Reasoning: Platforms like OpenAI Agent Builder enable you to build autonomous nodes that reason through multi-step conversations and define example dialogues to handle edge cases (source: YouTube Tutorials and YouTube 2).
- Testing: Real-time testing with sticky note feedback allows you to refine your agent’s responses before launch.
This phase ensures that your AI agent delivers the best possible user experience.
Step 6: Test, Deploy, and Monitor Your AI Agent
Before unleashing your AI agent into the world, comprehensive testing is crucial.
-
- Optimize for Accuracy and Cost: Keep an eye on large language model (LLM) usage and compare costs to avoid unexpected expenses (source: YouTube Tutorial).
-
- Deployment Options: Publish your agent across various channels—websites, WhatsApp, Slack, email, or even voice assistants using pre-made templates for faster rollout (source: YouTube Tutorials & YouTube 2).
- Monitoring & Iteration: Track your AI’s performance, gather user feedback, and iterate regularly to improve quality and fix issues (source: ClickUp Blog).
For those who prefer not to build from scratch, tools like ClickUp Brain offer pre-built AI automation with no coding required (source: ClickUp Blog).
Advanced Tips and Tools from Expert Tutorials
-
- Use OpenAI Agent Builder to easily create complex workflows, add logic and guardrails, then publish your AI agent quickly.
-
- Leverage Botpress or Zapier’s AI agents for complex multi-channel customer support or internal automations, while avoiding high LLM usage markups of 30-50%.
-
- Study OpenAI’s practical deployment guide which distills important lessons for product teams (source: OpenAI PDF Guide).
- Embrace ChatGPT Agent’s capability to “think and act” autonomously, empowering your AI agents with decision-making skills beyond simply answering prompts (source: OpenAI Introducing ChatGPT Agent).
Final Thoughts: The Future of AI Agents is in Your Hands
Building an AI agent with ChatGPT is no longer the stuff of science fiction. With powerful tools, accessible APIs, and rich ecosystems of no-code platforms available right now, anyone can create innovative agents that enhance productivity, delight customers, and automate complex tasks.
Remember to start with a clear purpose, choose the right technology, configure and customize your model carefully, build engaging user experiences, and continuously test and monitor your AI agent’s performance.
As you embark on your AI-building journey, keep your curiosity alive—there’s always a new capability to explore, such as integrating voice, adding autonomous tool use, or harnessing live data feeds.
The world of AI agents is wide open, and you have all the research-backed steps you need to confidently say: I built an AI agent with ChatGPT. So go ahead, create something amazing—because the future is intelligent.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
- What programming languages are best for building AI agents with ChatGPT?
Python is widely used due to its extensive AI libraries and ease of integration with the OpenAI API. Other languages can also be used, but Python remains the most popular.
-
- Can I build an AI agent without any coding experience?
Yes, no-code platforms like OpenAI Agent Builder, Botpress, and Zapier allow you to create AI agents via user-friendly interfaces.
-
- How can I make sure my AI agent stays up-to-date with the latest information?
Use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to connect your agent to live databases, documents, or APIs, so it can fetch current data instead of relying only on pre-trained knowledge.
-
- Is GPT-4 necessary for building AI agents?
GPT-4 is highly recommended because of its advanced understanding and reasoning capabilities, but earlier versions can also be used depending on your needs and budget.
-
- How do I monitor and improve my AI agent after deployment?
Track performance metrics, gather user feedback, and regularly update your data and rules. Tools like ClickUp Brain can assist with automation and monitoring.